Context
1.什么是Context
它是Android里的一个上帝类,启动四大组件、获取资源、获取类加载器等重要功能都通过Context 来完成,Activity、Service与Application也都派生自Context,Broadcast Receiver与Content Provider与Context 也有着密切的联系。
Context类图如下所示:
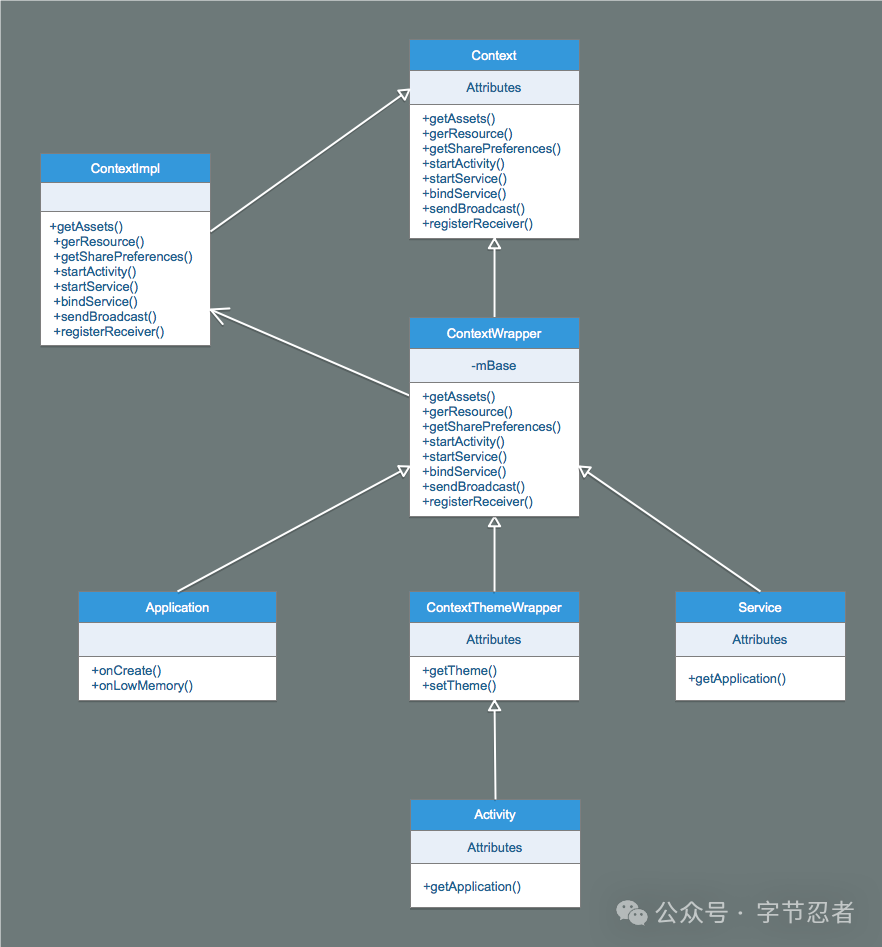
可以发现Context是个抽象类,它的具体实现类是ContextImpl,ContextWrapper是个包装类,内部的成员变量mBase指向的也是个ContextImpl对象,ContextImpl完成了 实际的功能,Activity、Service与Application都直接或者间接的继承ContextWrapper。
我们知道Context表示的应用的上下文环境,四大组件都与Context有密切的关系,在创建组件的时候会同时创建Context,并将两者进行绑定,我们来看看四大组件与 Context之间的关系。
2.Context与四大组件的关系
- Activity的创建流程
public final class ActivityThread {
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
// System.out.println("##### [" + System.currentTimeMillis() + "] ActivityThread.performLaunchActivity(" + r + ")");
ActivityInfo aInfo = r.activityInfo;
// 1. 获取LoadedApk对象。
if (r.packageInfo == null) {
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfo(aInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo,
Context.CONTEXT_INCLUDE_CODE);
}
ComponentName component = r.intent.getComponent();
if (component == null) {
component = r.intent.resolveActivity(
mInitialApplication.getPackageManager());
r.intent.setComponent(component);
}
if (r.activityInfo.targetActivity != null) {
component = new ComponentName(r.activityInfo.packageName,
r.activityInfo.targetActivity);
}
// 2. 创建Activity对象。
Activity activity = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = r.packageInfo.getClassLoader();
activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(
cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
StrictMode.incrementExpectedActivityCount(activity.getClass());
r.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(cl);
r.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
if (r.state != null) {
r.state.setClassLoader(cl);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate activity " + component
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
try {
// 3. 创建Application对象。
Application app = r.packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
// ...log
if (activity != null) {
// 4. 创建ContextImpl对象。
Context appContext = createBaseContextForActivity(r, activity);
CharSequence title = r.activityInfo.loadLabel(appContext.getPackageManager());
Configuration config = new Configuration(mCompatConfiguration);
if (r.overrideConfig != null) {
config.updateFrom(r.overrideConfig);
}
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Launching activity "
+ r.activityInfo.name + " with config " + config);
Window window = null;
if (r.mPendingRemoveWindow != null && r.mPreserveWindow) {
window = r.mPendingRemoveWindow;
r.mPendingRemoveWindow = null;
r.mPendingRemoveWindowManager = null;
}
activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token,
r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent,
r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config,
r.referrer, r.voiceInteractor, window);
if (customIntent != null) {
activity.mIntent = customIntent;
}
r.lastNonConfigurationInstances = null;
activity.mStartedActivity = false;
int theme = r.activityInfo.getThemeResource();
if (theme != 0) {
activity.setTheme(theme);
}
activity.mCalled = false;
if (r.isPersistable()) {
// 5. 执行Activity的onCreate()回调方法。
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state, r.persistentState);
} else {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state);
}
if (!activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
" did not call through to super.onCreate()");
}
r.activity = activity;
r.stopped = true;
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
activity.performStart();
r.stopped = false;
}
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
if (r.isPersistable()) {
if (r.state != null || r.persistentState != null) {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnRestoreInstanceState(activity, r.state,
r.persistentState);
}
} else if (r.state != null) {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnRestoreInstanceState(activity, r.state);
}
}
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
activity.mCalled = false;
if (r.isPersistable()) {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPostCreate(activity, r.state,
r.persistentState);
} else {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPostCreate(activity, r.state);
}
if (!activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
" did not call through to super.onPostCreate()");
}
}
}
r.paused = true;
mActivities.put(r.token, r);
} catch (SuperNotCalledException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to start activity " + component
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
return activity;
}
}Activity的创建流程如下所示:
获取LoadedApk对象。
创建Activity对象。
创建Application对象。
创建ContextImpl对象。
执行Activity的onCreate()回调方法。
Service的创建流程
public final class ActivityThread {
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {
// If we are getting ready to gc after going to the background, well
// we are back active so skip it.
unscheduleGcIdler();
// 1. 获取LoadedApk对象。
LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo);
Service service = null;
try {
// 2. 创建Service对象。
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
service = (Service) cl.loadClass(data.info.name).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate service " + data.info.name
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
try {
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Creating service " + data.info.name);
// 3. 创建ContextImpl对象。
ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, packageInfo);
context.setOuterContext(service);
// 4. 创建Application对象。
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault());
// 5. 执行Service的onCreate()回调方法。
service.onCreate();
mServices.put(data.token, service);
try {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to create service " + data.info.name
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
}Service的创建流程如下所示:
获取LoadedApk对象。 创建Service对象。 创建ContextImpl对象。 创建Application对象。 执行Service的onCreate()回调方法。
静态广播的创建流程
public final class ActivityThread {
private void handleReceiver(ReceiverData data) {
// If we are getting ready to gc after going to the background, well
// we are back active so skip it.
unscheduleGcIdler();
String component = data.intent.getComponent().getClassName();
// 1. 获取LoadedApk对象。
LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo);
IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
BroadcastReceiver receiver;
try {
// 2. 创建BroadcastReceiver对象。
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
data.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(cl);
data.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
data.setExtrasClassLoader(cl);
receiver = (BroadcastReceiver)cl.loadClass(component).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
// ...log
}
try {
// 3. 创建Application对象。
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
// ...log
// 4. 获取ContextImpl对象。
ContextImpl context = (ContextImpl)app.getBaseContext();
sCurrentBroadcastIntent.set(data.intent);
receiver.setPendingResult(data);
// 5. 回调onReceive()方法。
receiver.onReceive(context.getReceiverRestrictedContext(),
data.intent);
} catch (Exception e) {
// ...log
} finally {
sCurrentBroadcastIntent.set(null);
}
if (receiver.getPendingResult() != null) {
data.finish();
}
}
}静态广播的创建流程如下所示:
- 获取LoadedApk对象。
- 创建BroadcastReceiver对象。
- 创建Application对象。
- 获取ContextImpl对象。
- 回调onReceive()方法。
Content Provider的创建流程
public final class ActivityThread {
private IActivityManager.ContentProviderHolder installProvider(Context context,
IActivityManager.ContentProviderHolder holder, ProviderInfo info,
boolean noisy, boolean noReleaseNeeded, boolean stable) {
ContentProvider localProvider = null;
IContentProvider provider;
if (holder == null || holder.provider == null) {
if (DEBUG_PROVIDER || noisy) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Loading provider " + info.authority + ": "
+ info.name);
}
Context c = null;
ApplicationInfo ai = info.applicationInfo;
if (context.getPackageName().equals(ai.packageName)) {
c = context;
} else if (mInitialApplication != null &&
mInitialApplication.getPackageName().equals(ai.packageName)) {
c = mInitialApplication;
} else {
try {
// 1. 创建ContextImpl对象。
c = context.createPackageContext(ai.packageName,
Context.CONTEXT_INCLUDE_CODE);
} catch (PackageManager.NameNotFoundException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
if (c == null) {
// ...log
return null;
}
try {
// 2. 创建Content Provider对象。
final java.lang.ClassLoader cl = c.getClassLoader();
localProvider = (ContentProvider)cl.
loadClass(info.name).newInstance();
provider = localProvider.getIContentProvider();
if (provider == null) {
// ...log
return null;
}
if (DEBUG_PROVIDER) Slog.v(
TAG, "Instantiating local provider " + info.name);
// 3. 将ContextImpl对象绑定到Content Provider。
localProvider.attachInfo(c, info);
} catch (java.lang.Exception e) {
// ...log
return null;
}
} else {
provider = holder.provider;
if (DEBUG_PROVIDER) Slog.v(TAG, "Installing external provider " + info.authority + ": "
+ info.name);
}
IActivityManager.ContentProviderHolder retHolder;
synchronized (mProviderMap) {
if (DEBUG_PROVIDER) Slog.v(TAG, "Checking to add " + provider
+ " / " + info.name);
IBinder jBinder = provider.asBinder();
if (localProvider != null) {
ComponentName cname = new ComponentName(info.packageName, info.name);
ProviderClientRecord pr = mLocalProvidersByName.get(cname);
if (pr != null) {
// ...log
provider = pr.mProvider;
} else {
holder = new IActivityManager.ContentProviderHolder(info);
holder.provider = provider;
holder.noReleaseNeeded = true;
pr = installProviderAuthoritiesLocked(provider, localProvider, holder);
mLocalProviders.put(jBinder, pr);
mLocalProvidersByName.put(cname, pr);
}
retHolder = pr.mHolder;
} else {
ProviderRefCount prc = mProviderRefCountMap.get(jBinder);
if (prc != null) {
// ...log
if (!noReleaseNeeded) {
incProviderRefLocked(prc, stable);
try {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().removeContentProvider(
holder.connection, stable);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
//do nothing content provider object is dead any way
}
}
} else {
ProviderClientRecord client = installProviderAuthoritiesLocked(
provider, localProvider, holder);
if (noReleaseNeeded) {
prc = new ProviderRefCount(holder, client, 1000, 1000);
} else {
prc = stable
? new ProviderRefCount(holder, client, 1, 0)
: new ProviderRefCount(holder, client, 0, 1);
}
mProviderRefCountMap.put(jBinder, prc);
}
retHolder = prc.holder;
}
}
return retHolder;
}
}- 创建ContextImpl对象。
- 创建Content Provider对象。
- 将ContextImpl对象绑定到Content Provider。
- 通过上面的分析我们知道在四大组件创建的过程中,都需要创建ContextImpl对象与Application对象,Application对象都是通过LoadedApk的makeApplication()方法来完成的,但 是ContextImpl对象的创建方法却各不相同,我们来看一看。
Application的创建流程
通过上述内容可以发现,对于四大组件,Application的创建和获取方式也是不尽相同的,具体说来:
- Activity:通过LoadedApk的makeApplication()方法创建。
- Service:通过LoadedApk的makeApplication()方法创建。
- 静态广播:通过其回调方法onReceive()方法的第一个参数指向Application。
- ContentProvider:无法获取Application,因此此时Application不一定已经初始化。
- LoadedApk的makeApplication()方法如下所示:
public final class LoadedApk {
public Application makeApplication(boolean forceDefaultAppClass,
Instrumentation instrumentation) {
// Application只会创建一次,如果Application对象已经存在则不再创建,一个APK对应一个
// LoadedApk对象,一个LoadedApk对象对应一个Application对象。
if (mApplication != null) {
return mApplication;
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "makeApplication");
Application app = null;
String appClass = mApplicationInfo.className;
if (forceDefaultAppClass || (appClass == null)) {
appClass = "android.app.Application";
}
try {
// 1. 创建加载Application的ClassLoader对象。
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader();
if (!mPackageName.equals("android")) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER,
"initializeJavaContextClassLoader");
initializeJavaContextClassLoader();
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
}
// 2. 创建ContextImpl对象。
ContextImpl appContext = ContextImpl.createAppContext(mActivityThread, this);
// 3. 创建Application对象。
app = mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.newApplication(
cl, appClass, appContext);
// 4. 将Application对象设置给ContextImpl。
appContext.setOuterContext(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.onException(app, e)) {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate application " + appClass
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
// 5. 将Application对象添加到ActivityThread的Application列表中。
mActivityThread.mAllApplications.add(app);
mApplication = app;
if (instrumentation != null) {
try {
// 6. 执行Application的回调方法onCreate()。
instrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!instrumentation.onException(app, e)) {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to create application " + app.getClass().getName()
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
// Rewrite the R 'constants' for all library apks.
SparseArray<String> packageIdentifiers = getAssets(mActivityThread)
.getAssignedPackageIdentifiers();
final int N = packageIdentifiers.size();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
final int id = packageIdentifiers.keyAt(i);
if (id == 0x01 || id == 0x7f) {
continue;
}
rewriteRValues(getClassLoader(), packageIdentifiers.valueAt(i), id);
}
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
return app;
}
}Application的创建流程如下所示:
- 创建加载Application的ClassLoader对象。
- 创建ContextImpl对象。
- 创建Application对象。
- 将Application对象设置给ContextImpl。
- 将Application对象添加到ActivityThread的Application列表中。
- 执行Application的回调方法onCreate()。 👉 注:Application只会创建一次,如果Application对象已经存在则不再创建,一个APK对应一个LoadedApk对象,一个LoadedApk对象 对应一个Application对象。
Application对象的构建时通过Instrumentation的newApplication()方法完成的。
public class Instrumentation {
static public Application newApplication(Class<?> clazz, Context context)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException,
ClassNotFoundException {
Application app = (Application)clazz.newInstance();
app.attach(context);
return app;
}
}这里我们再注意一下ContextImpl的setOuterContext()方法,它用来设置外部Context,但是不同场景下设置的对象不同,具体说来:
- makeApplication():Outer Context设置的是Application。
- createBaseContextForActivity():Outer Context设置的是Activity。
- handleCreateService():Outer Context设置的是Service。
- BroadcastReceiver/Provider:Outer Context设置的是默认的ContextImpl。
